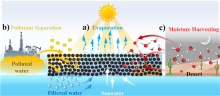
 03/31/2020Multifunctional Black Sand Aggregate Developed for Environmental-adaptive Solar-driven Purified Water Collection
03/31/2020Multifunctional Black Sand Aggregate Developed for Environmental-adaptive Solar-driven Purified Water Collection
A research group led by Prof. CHEN Tao at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has developed a multifunctional black sand aggregate for solar-driven purified water collection, which can adapt to diverse environments. The study was published in Nano Energy.
 03/25/2020Novel approach to Plastically Deform Magnetocaloric Alloys for Magnetic Refrigeration
03/25/2020Novel approach to Plastically Deform Magnetocaloric Alloys for Magnetic Refrigeration
Recently, a research group led by Prof. LIU Jian at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), cooperating with researchers at Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology and Inner Mongolia Normal University, developed a feasible open-die forging approach to plastically deform La-Fe-Si alloys for magnetic r...
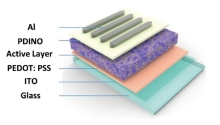 03/18/2020Researchers Develop a Fluorination Strategy to Fabricate High-efficiency Non-fullerene All-small-molecule Organic Solar Cells
03/18/2020Researchers Develop a Fluorination Strategy to Fabricate High-efficiency Non-fullerene All-small-molecule Organic Solar Cells
A research group led by Prof. GE Ziyi at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), has developed a BTEC-2F-based non-fullerene all-small-molecule organic solar cells (NFSM-OSCs) with a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 13.34%, which is among the highest PCE reported for NFSM-OSCs. The study was published...
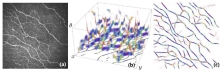 03/10/2020New Automated Method Proposed for Corneal Nerve Fiber Tortuosity Analysis
03/10/2020New Automated Method Proposed for Corneal Nerve Fiber Tortuosity Analysis
The Intelligent Medical Imaging (iMED) Group at the Cixi Institute of Biomedical Engineering, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), proposed a fully automated method for image-level corneal nerve fiber tortuosity estimation, contributing to the examination and diagnosis of eye-related diseases. The study was publ...
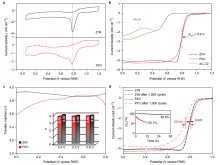 02/13/2020New Material to Surpass Traditional Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalysts
02/13/2020New Material to Surpass Traditional Oxygen Reduction Reaction Catalysts
A researcher group led by Prof. YANG Minghui at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), discovered that zirconium nitride (ZrN) catalysts could be a superior alternative to expensive platinum (Pt) catalysts for oxygen reduction. The study was published in Nature Materials.