 10/28/2024Novel Self-Cleaning Electrode Developed for Alkaline-Earth Metal Peroxide Synthesis
10/28/2024Novel Self-Cleaning Electrode Developed for Alkaline-Earth Metal Peroxide Synthesis
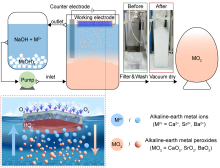
A Chinese research group has recently developed a novel self-cleaning electrode by constructing a micro-/nanostructure of a highly active catalyst with appropriate surface modification, achieving highly stable synthesis of alkaline-earth MO2 .
This study was published in Nature Nanotechnology.
 10/28/2024Highly Passivated TOPCon Bottom Cells Developed for Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cells
10/28/2024Highly Passivated TOPCon Bottom Cells Developed for Perovskite/Silicon Tandem Solar Cells
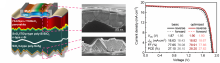
Prof. YE Jichun’s team from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), along with Prof. YU Xuegong’s team from Zhejiang University, has developed a highly passivated tunnel oxide passivating contact (TOPCon) bottom cell, achieving perovskite/silicon tandem solar cells (TSCs) with high open-circuit voltages...
 10/14/2024MAX Phases Boost Electrocatalytic Biomass Upgrading
10/14/2024MAX Phases Boost Electrocatalytic Biomass Upgrading
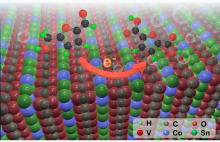
Prof. ZHANG Jian’s team at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), in cooperation with Prof. HUANG Qing’s team at NIMTE and Prof. LI Youbing at Soochow University, has developed a novel MAX phase with single-atom-thick cobalt layers, achieving high-efficiency electrocatalysis of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural (HMF...
 09/26/2024Novel Anti-Corrosion Anodes Facilitate Stable Seawater Electrolysis
09/26/2024Novel Anti-Corrosion Anodes Facilitate Stable Seawater Electrolysis
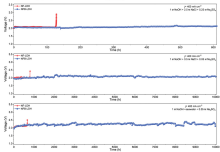
Prof. LU Zhiyi, Prof. CHEN Liang and coworkers at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have developed a novel anti-corrosion anode via chemical fixation of sulfate, achieving stable seawater electrolysis for over 10,000 h. The study was published in Advanced Materials.
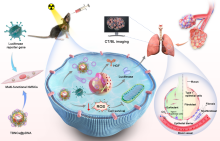 09/10/2024Novel Approach Proposed for Visualized Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapy by Transplanting Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells
09/10/2024Novel Approach Proposed for Visualized Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Therapy by Transplanting Engineered Mesenchymal Stem Cells
A research group led by Prof. WU Aiguo and Prof. LI Juan at the Laboratory of Advanced Theranostic Materials and Technology, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), developed a novel method for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) therapy by transplanting mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), which improved the therapeutic...