As one of the most efficient and environmentally-friendly approach for hydrogen production, water electrolysis consists of two half reactions, i.e., hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) and oxygen evolution reaction (OER). To accelerate the OER, Prof. CHEN Liang’s team at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has carried out series research on OER electrocatalysis combining experiment and theoretical calculaiton.
Compared with the alkaline water electrolysis, proton exchange membrane (PEM)-based water electrolysis shows distinct advantages like compact design, fast response, high voltage efficiency and high gas purity. However, the limited efficiency, low stability and high cost of acidic OER electrocatalysts still hinder the development of PEM-based water electrolysis.
Based on the previous studies on electrocatalysts for OER, researchers at NIMTE comprehensively summarized, classified and discussed the recently reported acidic OER electrocatalysts in terms of elements. The study was published in Advanced Materials.
Great emphasis was put on the OER mechanisms that fall into two categories, i.e., adsorbate evolution mechanism (AEM) and lattice oxygen oxidation mechanism (LOM), according to the origin of oxygen atoms.
The relationship between activity and stability of acidic OER electrocatalysts was discussed in detail. In addition, researchers proposed a stability test protocol to evaluate the intrinsic activity degradation.
The current development challenges and unsolved issues of acidic OER electrocatalysts were discussed, such as the usage of carbon-based materials. The suggestions for the synthesis of high-performance acidic OER electrocatalysts for PEM-based water electrolysis were also presented.
The work was supported by the“From 0 to 1” Innovative program of CAS (No. ZDBS-LY-JSC021), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (Nos. LD21E020001 and LY21E020008), National Natural Science Foundation (Nos. 51872306 and 52271232), K. C. Wong Education Foundation (GJTD-2019-13), Ningbo S&T Innovation 2025 Major Special Program (Nos. 2019B10046 and 2020Z107) and the Youth Innovation Promotion Association of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 2020300).
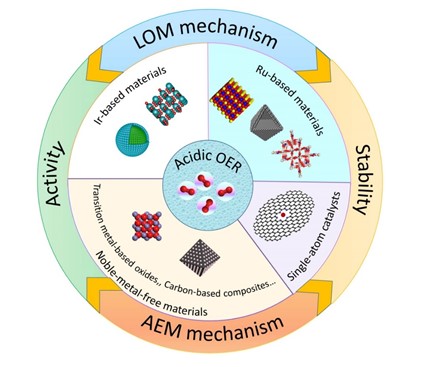
Fig. The classification and the relationship between activity/stability of acidic OER electrocatalysts (Image by NIMTE)
Contact
LIN Yichao
Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering
E-mail: yclin@nimte.ac.cn

