A research group led by Prof. WANG Junqiang at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have developed a combinatorial high-throughput strategy to screen superior catalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER). The research work has been published in ACS Catalysis.
Thanks to the excellent features of low cost, high catalytic activity and good durability, catalysts based on multiple non-noble metals, such as Ni and Co alloys, have attracted increasing attention worldwide in the research realm of HER or oxygen evolution reaction (OER). However, due to the vast compositional space of multicomponent alloys which requires considerable work on catalyst fabrication and performance test, it remains challenging to identify the optimal catalyst for HER both computationally and experimentally.
Based on previous studies, researchers at NIMTE selected the non-noble elements Ni and Co as the dominant alloy components with Ti as the additional alloy element, thus tailoring the hydrogen evolution. Through magnetron co-sputtering deposition, researchers synthesized the ternary Ni-Co-Ti film library.
Researchers proposed the high-throughput bubble screening method to identify the superior multicomponent alloys employed as the high-performance HER catalysts. The overall screening efficiency has been improved by more than 10000 times as compared with the traditional time-consuming and labor-intensive trial-and-error methods.
In addition, the parallel electrochemical analysis was conducted, indicating that among the broad-phase diagram with 39% < Ni < 69%, 22% < Co <50%, and 5.5% < Ti < 20%, the Ni56.5Co35Ti8.5 alloy possesses the optimal catalytic performance.
Moreover, the underlying mechanisms has been studied, which revealed that the low atomic packing density and low electron binding energy contribute to the high catalytic activity in HER.
The combinatorial high-throughput strategy proposed in this study showed great potential to be extended to the catalyst exploration in higher composition alloy systems and even for OERs.
This work was financially supported by the National Key R&D Program of China (No. 2018YFA0703600), the Youth Innovation Promotion Association CAS (No. 2019296), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. NSFC 51922102, 52071327, 52001319, and 92163108), the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. LR22E010004 and 2022C01023), and the Ningbo 2025 Science and Technology Innovation Project (No. 2019B10051).
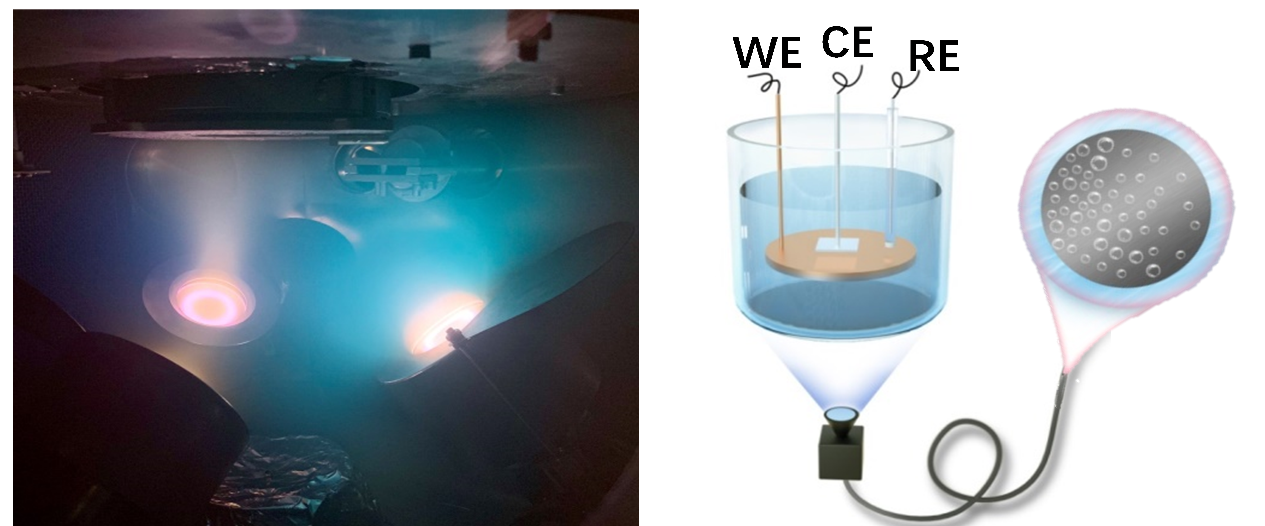
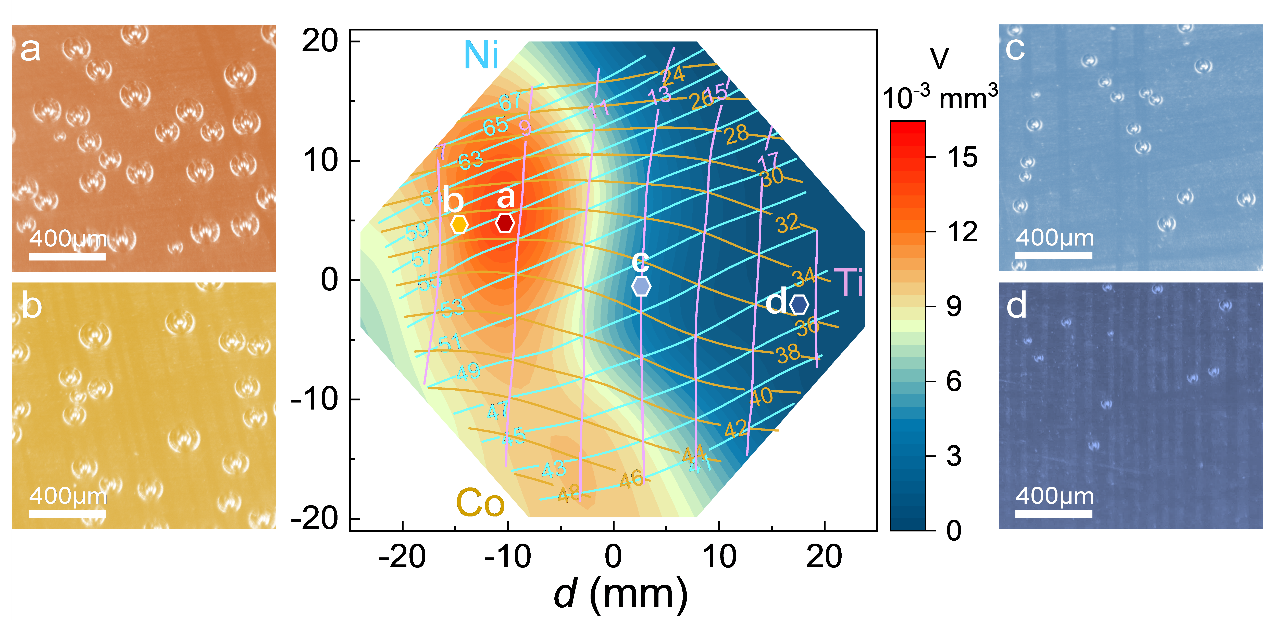
Fig. The schematic illustration of high-throughput bubble screening method and a corresponding example in Ni-Co-Ti ternary catalysts (Image by NIMTE)
Contact
WANG Junqiang
Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering
Email: jqwang@nimte.ac.cn

