Researchers at Key Laboratory of Marine Materials and Related Technologies, Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), have established a thermodynamic database of novel NiSiAlY alloys, and thus facilitating the research and development (R&D) of NiSiAlY Alloys. The findings were published in Journal of Materials Science & Technology (Part I and Part II).
MCrAlY (M=Fe, Co, Ni, or a mixture) alloys are widely employed as bond layers or single layers of thermal barrier coatings (TBCs) for hot-section components of aircraft or in power-generation turbines, thanks to the excellent high-temperature oxidation and corrosion resistance. These outstanding properties are demonstrated attributed to the protection from oxidation and corrosion provided by the stable, dense and continuous oxide films, which are mainly composed of Al2O3 and Cr2O3.
However, oxides form discontinuously on MCrAlY surface under harsh marine salt-spray environment, since Cr2O3 was highly reactive with NaCl and H2O at 400-700 ℃.
Towards this end, researchers at NIMTE replaced Cr with Si, due to that Si has significant solubility in bcc_B2 (β-NiAl) and L12 (γ’-Ni3Al) and can function as an active element to improve the performance of high-temperature coatings, which makes the NiSiAlY alloys promising candidates for high-temperature corrosion resistance in harsh marine salt-spray environment.
Through coupling the CALPHAD (CALculation of PHAse Diagrams) approach and first-principles calculations, the thermodynamic descriptions of the ternary compounds were obtained. Based on these data, a self-consistent thermodynamic database of NiSiAlY alloys was established. Thus the material R&D of the novel NiSiAlY alloys was promoted in terms of the composition screening and technology optimizing.
This so-established database may provide constructive guidance for the R&D of novel NiSiAlY alloys, which can protect materials from corrosion under harsh salt-spray environment.
In addition, the researchers at NIMTE proposed the selection of the NiSiAlY alloys for serving in marine salt-spray environment with three constraints, i.e., outstanding mechanical property, good high-temperature anti-oxidation and excellent corrosion resistance.
Combining with the calculated Al-Ni-Si-Y phase diagrams concerning the content variations of Al and Si, a compositional range corresponding to the L12+bcc_B2+Ni5Y ternary phase region at temperatures ranging from ~500 to ~1000 ℃ has been proposed. These predictions were further validated by key experiments, indicating that the model-based description of the Al-Ni-Si-Y system can guide the R&D of the novel NiSiAlY alloys.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51971235), Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No. LQ20E010004), National Science and Technology Major Project (No. 2017-VII-0012-0107) and Ningbo 3315 Innovation Team (No. 2019A-18-C).
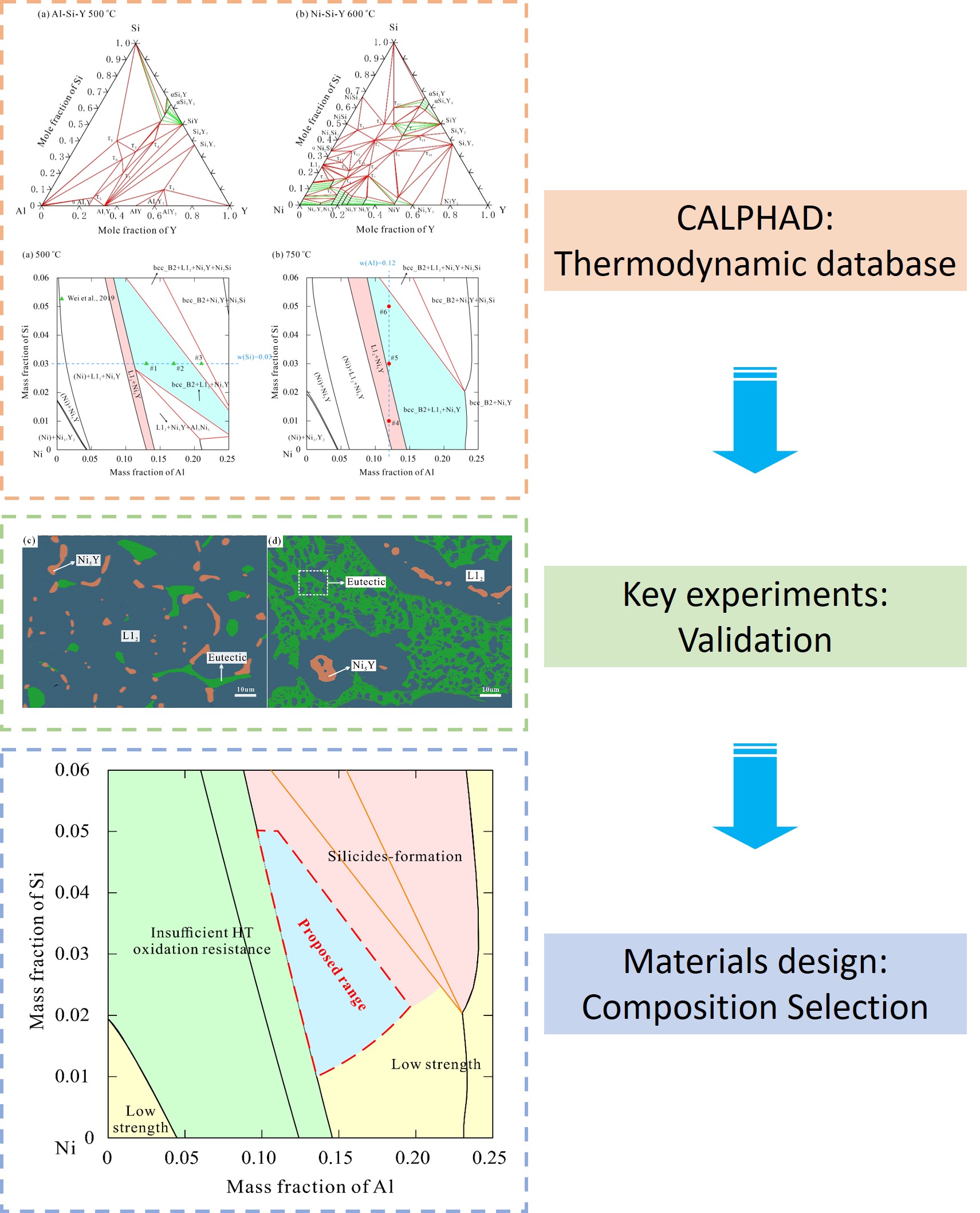
Fig. Design of novel NiSiAlY alloys based on phase diagrams (Image by NIMTE)
Contact
CHANG Keke
Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering
E-mail: changkeke@nimte.ac.cn

