A research group led by Prof. ZHUGE Fei at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) developed an all-optically controlled (AOC) analog memristor, whose memconductance can be reversibly tuned by varying only the wavelength of the controlling light. The study was published in Advanced Functional Materials.
As the next generation of artificial intelligence (AI), neuromorphic computing (NC) emulates the neural structure and operation of the human brain at the physical level, and thus can efficiently perform multiple advanced computing tasks such as learning, recognition and cognition.
Memristors are promising candidates for NC thanks to the feasibility of high-density 3D integration and low energy consumption. Among them, the emerging optoelectronic memristors are competitive by virtue of combining the advantages of both photonics and electronics. However, the reversible tuning of memconductance depends highly on the electric excitation, which have severely limited the development and application of optoelectronic NC.
To address this issue, researchers at NIMTE proposed a bilayered oxide AOC memristor, based on the relatively mature semiconductor material InGaZnO and a memconductance tuning mechanism of light-induced electron trapping and detrapping.
The traditional electrical memristors require strong electrical stimuli to tune their memconductance, leading to high power consumption, a large amount of Joule heat, microstructural change triggered by the Joule heat, and even high crosstalk in memristor crossbars.
On the contrary, the developed AOC memristor does not involve microstructure changes, and can operate upon weak light irradiation with light power density of only 20 μW cm-2, which has provided a new approach to overcome the instability of the memristor.
Specifically, the AOC memristor can serve as an excellent synaptic emulator and thus mimic spike-timing-dependent plasticity (STDP) which is an important learning rule in the brain, indicating its potential applications in AOC spiking neural networks for high-efficiency optoelectronic NC.
Moreover, compared to purely optical computing, the optoelectronic computing using our AOC memristor showed higher practical feasibility, on account of the simple structure and fabrication process of the device.
The study may shed light on the in-depth research and practical application of optoelectronic NC, and thus promote the development of the new generation of AI.
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 61674156 and 61874125), the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. XDB32050204), and the Zhejiang Provincial Natural Science Foundation of China (No. LD19E020001).
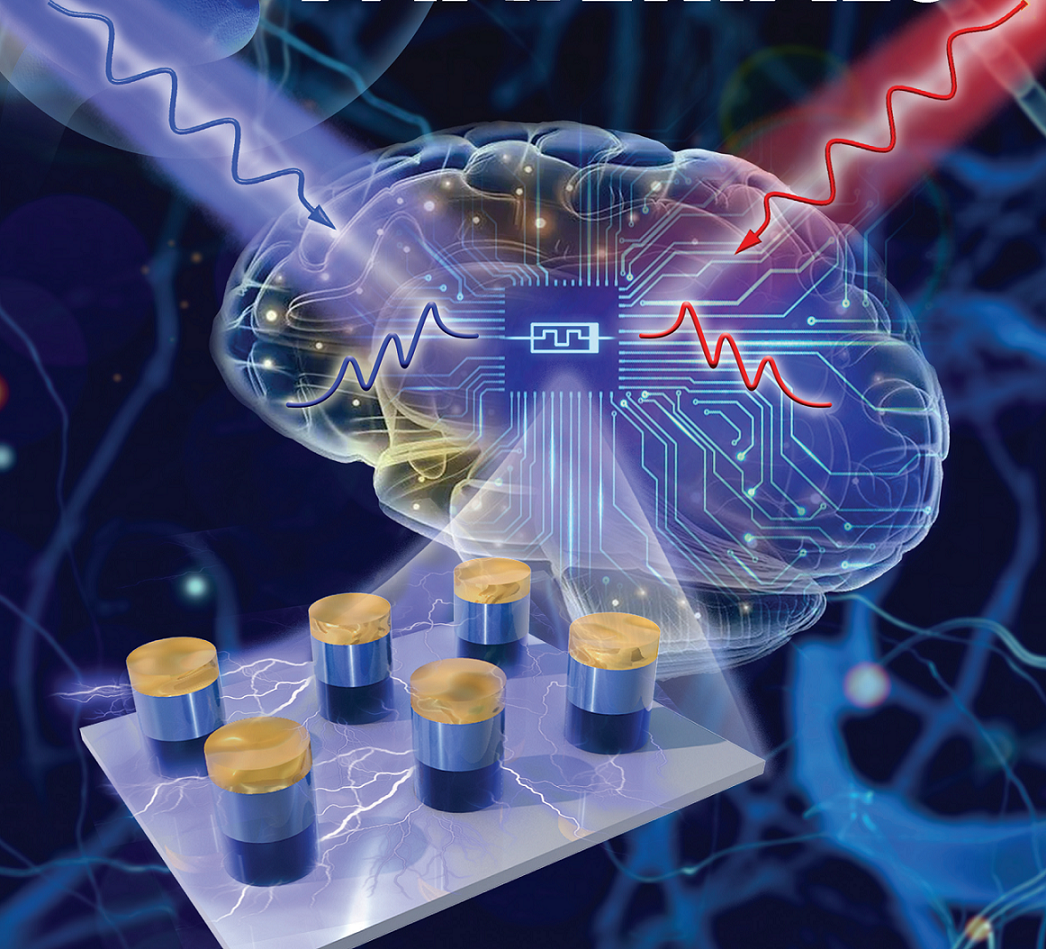
Fig. The all-optically controlled memristor developed for optoelectronic neuromorphic computing (Image by NIMTE)
Contact
ZHUGE Fei
Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering
E-mail: zhugefei@nimte.ac.cn

