A research group led by Prof. HUANG Qing at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) have developed a general Lewis acidic etching route for preparing MXenes with enhanced electrochemical performance in non-aqueous electrolyte, in cooperation with Université de Toulouse, Sichuan University and LiU. The study was published in Nature Materials.
Two-dimensional (2D) transition metal carbides/nitrides (MXenes) are one of the newest members of 2D material family, which have attracted great attention as energy storage materials. MXenes are prepared by selective etching of the A-layer elements in MAX-phase precursors. Since the first report of Ti3C2 synthesis in 2011, the preparation of MXenes have mainly involved the selective etching of the A-layer of MAX phases by fluoride ion solution, such as HF (hydrogen fluoride). It is hazardous and the -F group affects electrochemical performance, which has limited the large-scale production and applications of MXenes.
To achieve a fluorine-free route preparation of MXenes, researchers at NIMTE proposed a general strategy to synthesize 2D MXenes through high-temperature molten salt Lewis acid route (experiment demonstration). By constructing the Gibbs free energy mapping of the redox potential of cations with A-site elements and the stripping reaction of A-site element under high-temperature molten salt environment, an A-site etching method of MAX phases in Lewis acidic melts was proposed.
In addition, they also carried out a systematic electrochemical energy storage study of Ti3C2Tx MXenes obtained through Lewis acid molten salt in LiPF6 organic electrolyte. The synthesized MXene showed excellent cyclic stability, high capacity, high rate charge and discharge, and large potential window.
Different from the HF etching, the high-temperature molten salt lewis acid stripping method facilitates the safe operation in the laboratory and the surface chemistry tunning.
The study may promote the fabrication of Mxenes, promising MXenes a bright future for application in electrochemical energy storage devices, such as batteries and lithium-ion capacitors.
This work was supported by Ningbo Top-talent Team Program, International Partnership Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (No. 174433KYSB20190019), National Natural Science Foundation of Chinanos (No. 21671195, 91426304, 51902320 and 51902319), and the Leading Innovative and Entrepreneur Team Introduction Program of Zhejiang.
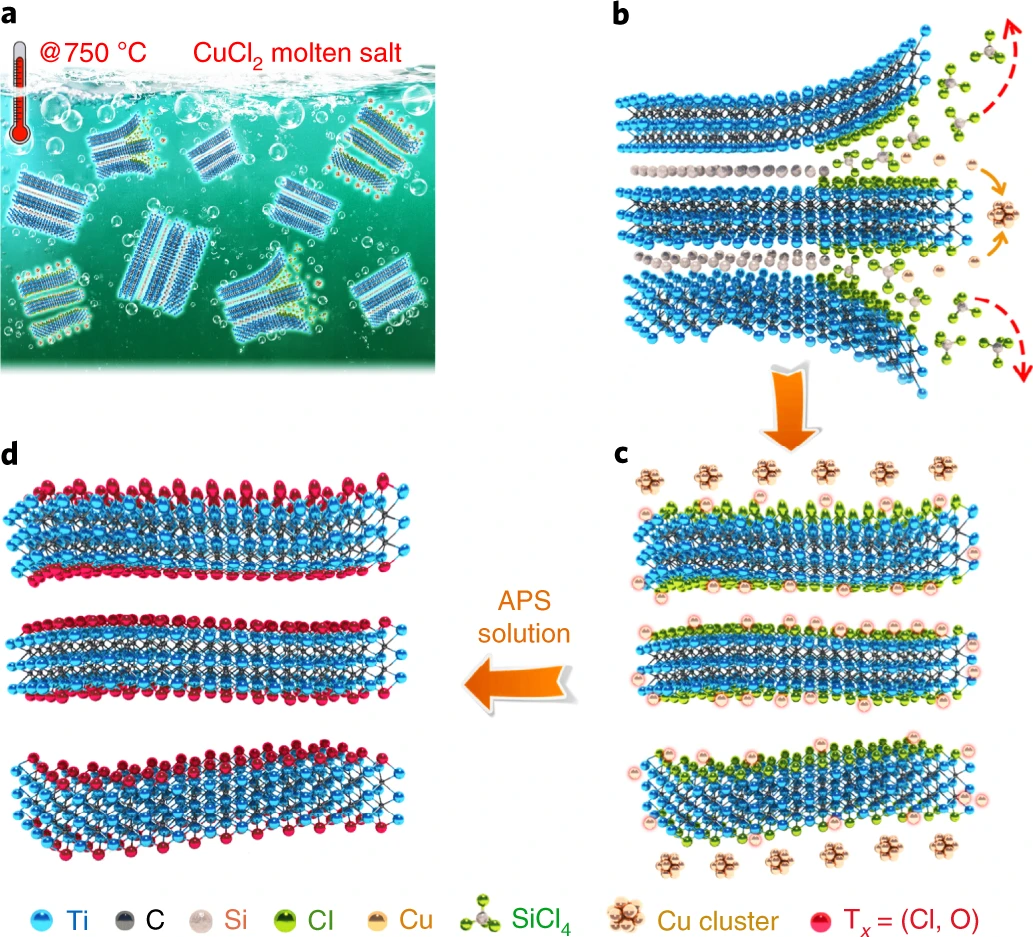
Fig. Schematic of Ti3C2Tx MXene synthesis by stripping lewis acid from molten salt at high temperature (Image by NIMTE)
Contact
HUANG Qing
Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering
E-mail:huangqing@nimte.ac.cn

