Polylactide (PLA) is one of the most popular researches on bio-based, biodegradable green polymers for the last decade. However, PLA with high molecular weight still has some disadvantages such as 1) requirements of high purity monomer, complex process and precisely controlled reaction condition for PLA synthesis, resulting in high cost; 2) poor flexibility and heat resistance; 3) few varieties. Researchers focus their attention on some physical and chemical methods to improve the performance of PLA such as blend, copolymerization or surface modification, etc. Although being potentially large scale (millions of tons) raw materials for the modern world wide polyurethane industry, low molecular weight PLA polyols get low attention. Then a series of high performance PLA-based polyurethanes can be obtained by the reaction with isocyanates, which would open up a new path for high-efficient utilization of PLA.
The advanced coatings and adhesives technology group led by Professor Haibin Yu from Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology & Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences has successfully developed a series of PLA polyols (CN201510054929.7; 201510504652.3; 201510504687.7) by solving the technical problems on high residual monomer and acid value, which achieved world's first industrial preparation of polylactide polyols with high quality at the pilot production in the 600 kg level (Figure 1). The obtained PLA polyols have many advantages such as controllable molecular weight, narrow molecular weight distribution, variety, simple process, low acid value, low residual monomer, low cost, etc. Then a series of high performance bio-based polyurethanes (bio-PUs) were synthesized from PLA-based polyols, different diisocyanates (TDI, MDI, HDI, IPDI) and chain extenders by solution polymerization, in which different soft and hard segments are used to adjust their transition temperatures and mechanical properties (CN201510659107.1; RSC Advances, 2016, 6, 17888-17895; Chinese Journal of Polymer Science, 2016, 34(7), 901-909;Chinese Journal of Biotechnology, 2016, 32(6), 831-838). Among them, MDI-based bio-PUs have the highest Tg (43.8 °C), tensile strength (23.5 MPa) and modulus (380.8 MPa), while HDI-based bio-PUs have the lowest Tg (21.4 °C) and highest elongation at break (580%). Synthesized bio-PUs demonstrate better mechanical properties, closed to petroleum-based commodities. Furthermore, the obtained bio-PUs display good shape memory properties at physiological temperature and cytocompatibility. Therefore, these bio-PUs are promising for applications in biomedical fields.
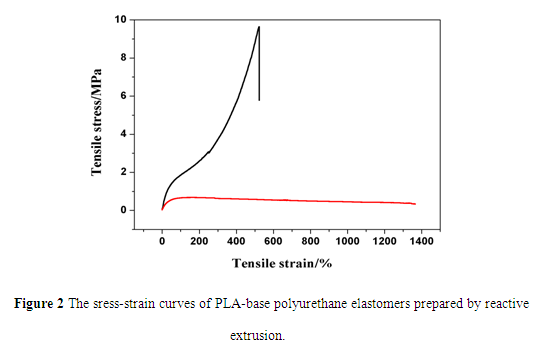
Based on the above research, this research team recently has achieved a step green preparation of PLA-base polyurethane elastomers by reactive extrusion, avoiding the use of organic solvents, easy to scale production, which can be applied in high-end fields such as soft 3D printing materials, biomedical devices, etc. In addition, the mechanical properties of the elastomers can be adjusted by extrusion conditions (Figure 2). At present, this research team already has the green industrialized preparation technology from the green raw material PLA polyols to PLA-based polyurethanes. This research achievement will have the obvious promotion function to the industry application of PLA.
This work was supported by the Ningbo key project (Grant No. 2014B10023) and Shenzhen Esun Industrial Co., Ltd.

Dr.Lin Gu: gulin@nimte.ac.cn
Prof. Haibin Yu: haibinyu@nimte.ac.cn
All Images by ![]()

