Hydrogels are three-dimensional hydrophilic polymer networks formed by chemical or physical crosslinking. They possess both fluidityas liquids and shape-stabilityas solids.Drugs can be embedded into them and released in a controlled manner, making hydrogelsvery usefulmedical materials.
Silver ions are strongly antibacterial. For instance, silver nitrate and sulfadiazineexhibited strong killing effect towards Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative bacteria and mycetes.Silver nanocrystals showed better killing effect than traditional silver ion sterilant. Silver nanocrystals are widely used in curing dermatologic diseases such as burn wounds and acnes.
Prof. Xuedong Wu’s group from Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, CAS, prepared polythioether dendritic monomers and used them to elaborate high Ag content poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide) hydrogels. Every polythioether dendritic monomers is composed of six thioether bonds. These bonds are oxidation-sensitive. They can be oxidized into sulfoxide bonds under mild oxidants like H2O2, sodium hypochlorite and etc.,. And they turned rapidly from hydrophobic nature into strongly hydrophilic nature.The sulfur atoms are able to strongly bind heavy metal ions. And the chelation effect could be further strengthened by the claw-like shape of dendritic monomers.The introduction of polythioether dendrons endows the hydrogels with these properties: Via setting up the oxidation degrees, the lower critical solution temperatures can be set up facilely and rapidly under the range of 31.0~88.1 oC.the loading capacity of Ag is greatly improved, demonstrated by the fact that the loading capacity of the hydrogel containing 2.5 mol% of polythioether monomers or polysulfoxide monomers is 55.0 mg (Ag)/g (gel)or 67.2 mg (Ag)/g (gel), respectively,19 or 23 times higher than those of the pristine poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide); upon in situreduction, well-dispersedAg nanoparticles about 10 nm are acquired. Based on these features,current research efforts are dedicated to the smart control of the release rate of Ag ions by setting up LCSTs.
More details of this work can be found in Polymer Chemistry, 2015, 6, 625-632.
Fig. 1 Presentation of oxidation of the hydrogels and the formation procedure of the Ag nanocrystals.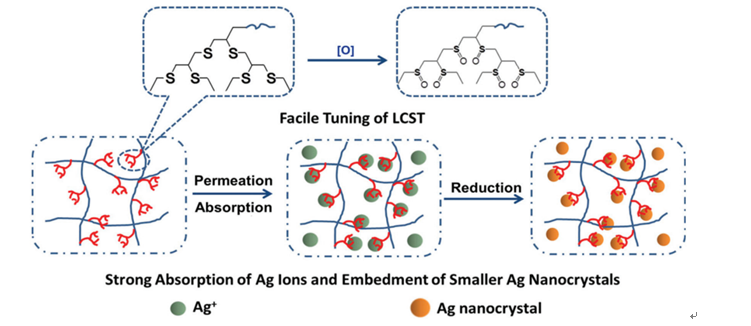
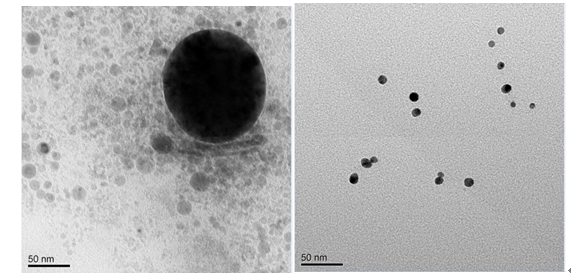
Fig. 2 TEM pictures of the Ag particles in the pristine hydrogels (left) and the Ag nanocrystals in the hybridhydrogels containing 5 mol% of polythioether dendritic monomers (right).
Prof. Xuedong Wu: xdwu@nimte.ac.cn Dr. Jin Han: hj@nimte.ac.cn
Research Staff Url: http://english.nimte.cas.cn/pe/fas/200909/t20090929_44484.html
All Images by ![]()

