The inherent unique structural features and exceptional properties of graphene, combined with the ability to uniformly deposit thin nanolayers or coatings using vacuum cold spraying (VCS) technology, give rise to enormous potential for graphene in thin film functional coatings for electronics, corrosion-inhibiting, and even biomedical implant. The growing availability of graphene enables research in many new technology areas.
Recently, Hua Li’s group at the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering, the Chinese Academy of Sciences successfully deposited graphene-containing nanocomposite coating for biomedical implant coatings using VCS at room temperature. VCS, a method based on shock-loading solidification, is a novel and promising spray technique which enables deposition of nano/submicro-sized powder on various substrates in a vacuum chamber. The room temperature VCS deposition offers advantages of efficiently transferring the microstructure of feedstock powder to the as-deposited film/coating without significant crystal grain growth or structural changes. Microstructural examination from cross-sections of the obtained coatings suggests that apart from its even distribution within the coatings, graphene nanosheets (GN) stays in the first layer intimately contacting with the substrate (Fig. 2 a, b). The particular structural feature of starting hydroxyapatite(HA)-GN composite powder (Fig.1) is apparently retained in the coating.
The research appeared on the cover of the Journal of Thermal Spray, authored by Yi Liu, Jing Huang, and Hua Li (J Therm Spray Tech 2014, 23, 1149-1156).

Fig.1 The cover of the Journal of Thermal Spray, Volume 23 Number 7-October 2014
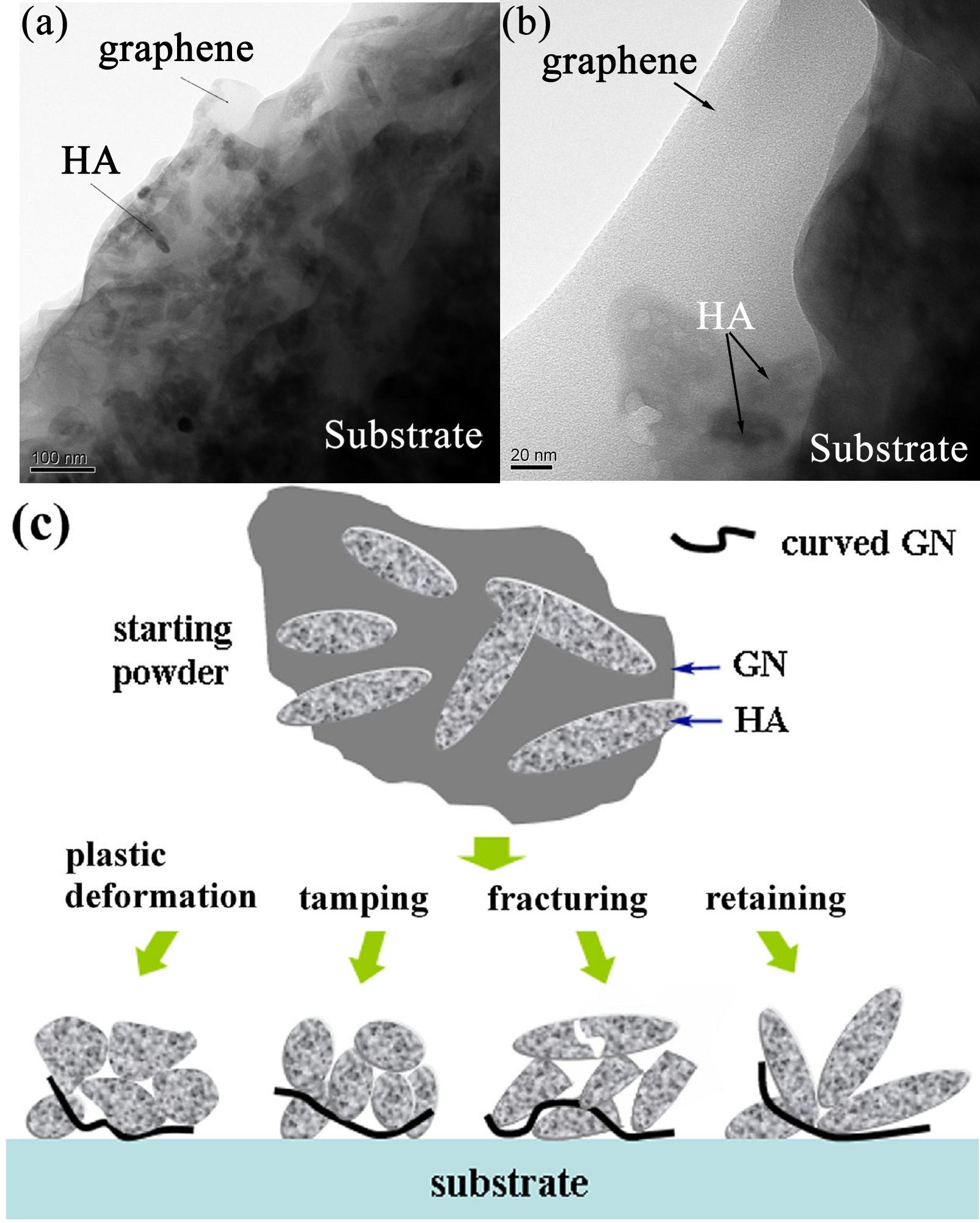
Fig.2 TEM images of the HA-GN coating showing presence of GN in the first layer that intimately contacts with the substrate (a,b), and (c) schematic illustration demonstrating the formation mechanisms of the HA-GN nanocomposite coating
Keywords: vacuum cold spray, graphene, nanocomposite coatings, microstructure
Prof. Hua Li lihua@nimte.ac.cn
Research Group Url:http://english.nimte.cas.cn/rh/rd/ssfc
All Iamges by ![]()

