The increasing deployment of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind power requires a commensurate increase in energy storage capacity to integrate them into the grid. Batteries are good means of storing the electricity in the form of chemical energy. Owning to good safety, high ionic conductivity and low cost, aqueous ion batteries are potentially advantageous over their organic counterparts for large-scale energy storage. In contrast to lithium, sodium is more abundant and economical. Therefore, sodium-ion battery is considered as a potential alternative to current Lithium-ion battery for large-scale energy storage. However, materials suitable for aqueous sodium-ion battery are very limited, which is identified as the major hurdle for the widespread application.
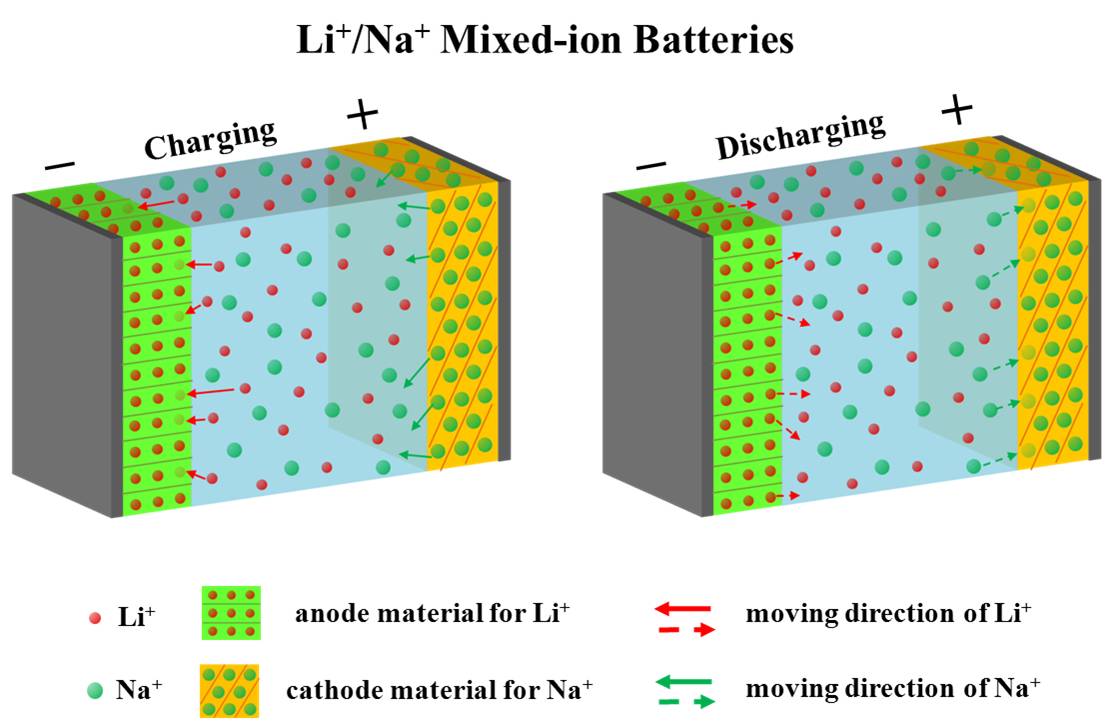
To overcome above hurdle, a team led by Prof. Zhaoping Liu from the Advanced Li-ion Battery Engineering Lab, the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Science (NIMTE), the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), firstly proposed an innovative concept of Li+/Na+ mixed-ion electrolytes to construct rechargeable batteries, as shown in Figure 1. In such batteries, one side involves the immigration of Li+ between electrolytes and electrode, and the other one refers to the exchange of Na+ between electrode and electrolytes. They are unlike traditional “rocking-chair” lithium-ion batteries. Thus Li+/Na+ mixed-ion batteries pave a new route to the energy storage system.
 |
|
Figure 1 Schematics of Li+/Na+ mixed-ion battery. |
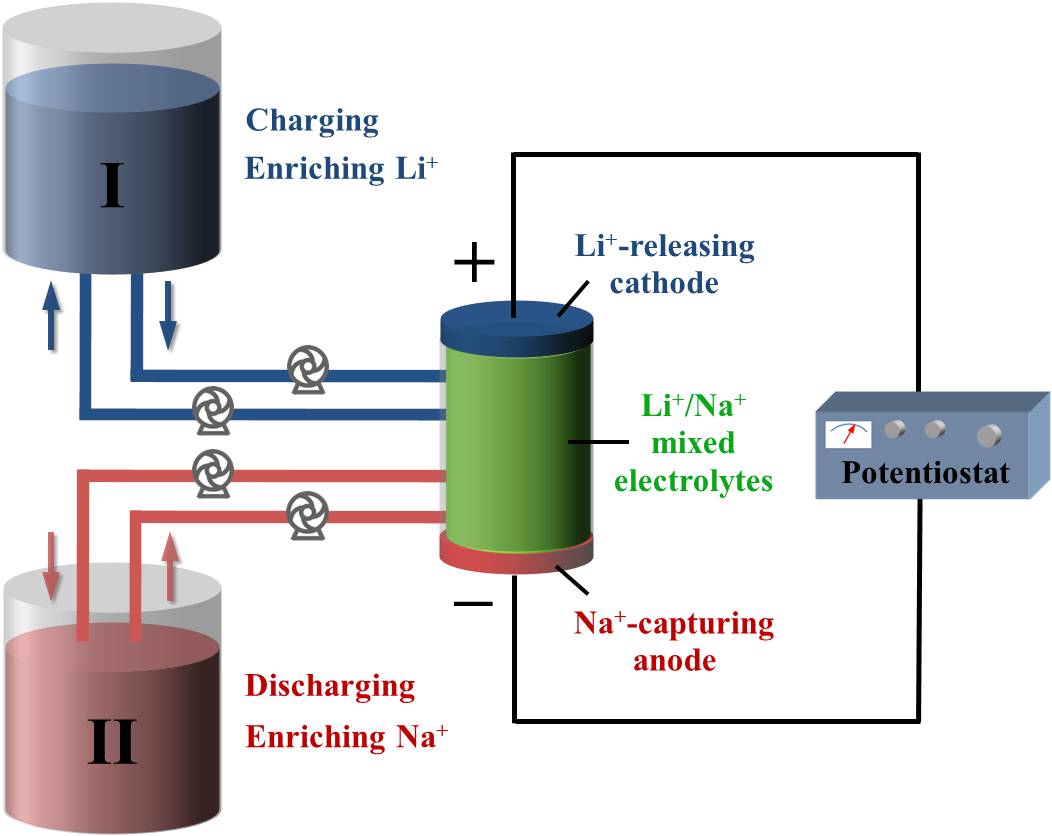
As well, Li+/Na+ based mixed-ion batteries can be utilized to separate Li+ and Na+ based on the unique mechanism. By using a simple setup in Figure 2, Li+ and Na+ can be respectively enriched throughout repetitive charging and discharging steps. Compared with current chemical separation techniques, this electrochemical technique is simple, green and energy efficient. It offers hugely promising application in the field of Li+/Na+ separation in sea water and brine lakes.
 |
|
Figure 2Schematic representation of the working principle on the separation of Li+ and Na+ by the mixed-ion battery. |
The relevant results have been published as an article in Scientific Reports (DOI.10.1038/srep01946).
Professor Zhaoping Liu liuzp@nimte.ac.cn
Research Group url: http://english.nimte.cas.cn/rh/rd/battery/
All Images by 

