Nitrogen-doped carbon nanomaterials have become one of the most interesting topics in the fields of nanomaterials and energy chemistry. The doped nitrogen atoms which having one more valence electron can greatly affect the electronic structure of the graphitic lattice and enrich the surface with many chemically active groups such as pyridine, pyrrole, pyridine-oxide, etc.
Among the nanostructures of carbon materials, hollow carbon spheres (HCS) possess advantages of low density, high specific surface area, and structural feature of filling cavity, which resulting in their broad applications in drug delivery, nanoreactor, lithium-ion battery, enzymes immobilization and other fields. HCS have been usually synthesized via chemical vapor deposition, arc discharge and hydrothermal methods, which are suffered from the great difficulty in controlling size, shell thickness, surface roughness, graphitization degree, etc.
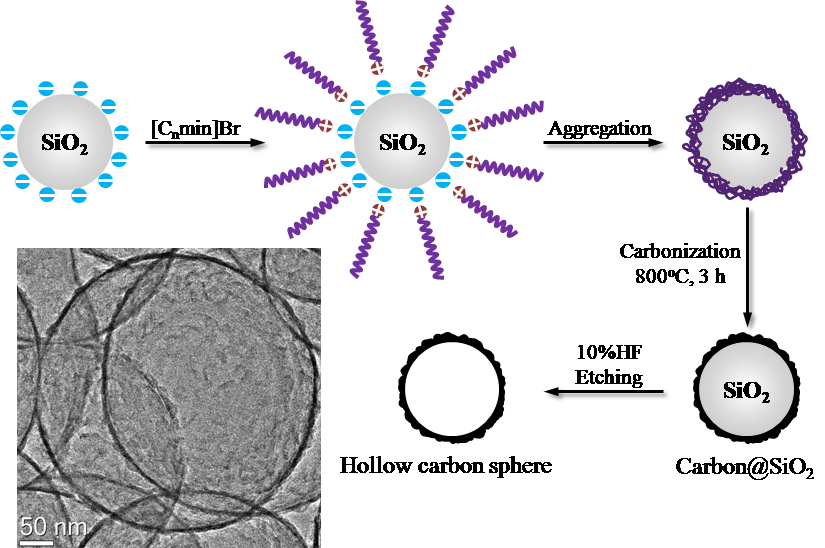
A new synthesis method of nitrogen-doped HCS has been explored by Professor Jian Zhang’s group of the Ningbo Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE) and the researchers in the Hebei University of Science and Technology (HUST), which is to use nitric ionic liquids as the carbon and nitrogen sources, assemble them into thin layers on the monodispersed silica as the template, and then remove silica template after high temperature graphitization treatment (Fig.1).
 |
|
Fig.1 Schematic of the formation process of hollow carbon spheres. |
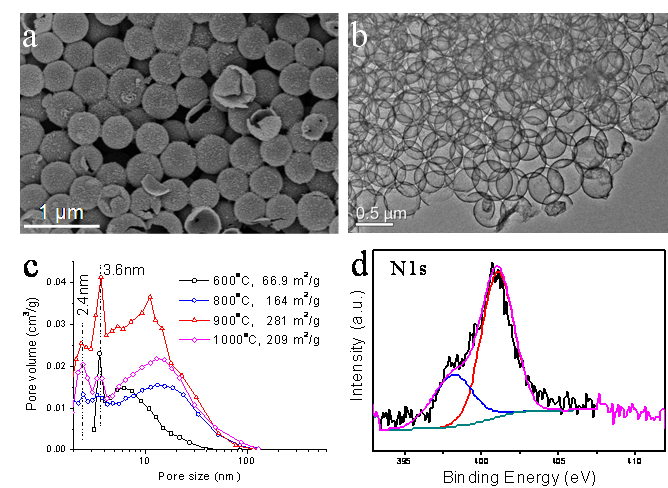
The as-synthesized HCS has many attractive features including huge size (up to 900 nm in diameter), thin wall (5-12 nm), mesoporous structure and nitrogen doping (3.2% nitrogen) (Fig. 2).
 |
|
Fig. 2 Characterization results of hollow carbon sphere. (a) SEM and (b) TEM images; (c) Infrared and (d) N1s spectra. |
This work may provide new ideas for the synthesis and application of novel carbon structures with heteroatom dopants.This research has been published in the first issue of the Journal of Materials Chemistry A 2013 (DOI: 10.1039/C2TA01013E) by Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC).
Professor Jian Zhang jzhang@nimte.ac.cn
All Images by![]()

