With the increasing number of applications of carbon fiber (CF) reinforced resin composites in the aeronautical, automotive, sports goods industries, new energy and transport fields, etc., the waste composites have reached a significant level in recent years. Due to their three-dimensional network structure, the thermosetting resin based composites cannot be melted or dissolved to recover. Simple treatment or mechanical recycling of the scrap composites with a high content of CFs would lead a great loss of valuable materials. A variety of technologies have thus been investigated for chemically recycling high value CF from scrap polymer composites.
Nevertheless, these technologies usually require high temperature, long reaction times, nasty solvents (e.g., nitric acid), or rigorous conditions, and only work to some types of composites. Developing methodologies for the chemical recycling of thermosetting composites into useful CFs and organic compounds remains as one of the most important yet challenging issues in polymer and materials science.
To develop new avenues to recycle CF reinforced epoxy (EP) resin composites, Dr. Juan Li and her group from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), CAS has undertaken the related research since 2010. After two years’ exploration, an efficient solution was found for the chemical recycling of CF/EP composites through oxidative degradation under mild conditions. Clean CF was obtained after reacting at 60 °C for 30 min. The decomposition ratio of EP was above 90%, and the strength of recycled CF retained more than 95% of its original strength. Useful organic compounds were produced by controlling the reaction process. A self-accelerating phenomenon was discovered and its mechanism was suggested (Fig.1).
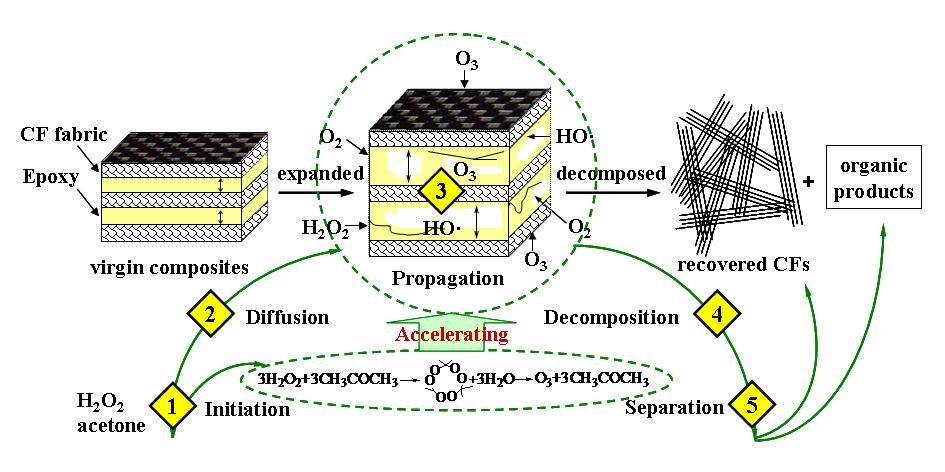 |
|
Fig.1 self-accelerating mechanism for decomposition of composites |
The research results have been published in Green Chemistry (2012,14, 3260-3263), a patent has been authorized (ZL 2010 1 0274001.7), and two have been filed (201110102003.2 and201110257706.2).
Dr. Juan Li lijuan@nimte.ac.cn
All Images by ![]()

