A special type of dialysis membrane module, called dialyzer (Fig.1), is used in the pressure-driven hemodialysis process to remove excess waste products and water from the body. Treatments take from four to six hours and usually are performed three times a week. The materials requirement for blood purification is very strict, and therefore, membrane materials which can be used in clinical application are actually very few. Cellulose and polysulfone are two main membrane materials, and the related technologies are now monopolized by a few companies like Fresenius, Gambro, and Baxter.
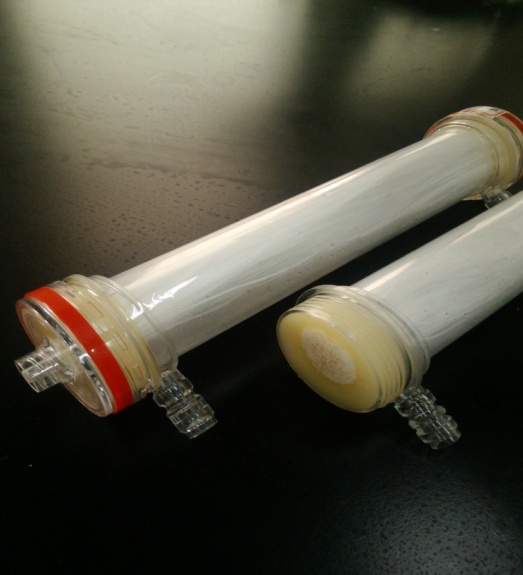 |
| Fig.1 PLA module for hemodialysis |
Recently, the functional membrane group led by Professor Lixin Xue and Associate professor Fu Liu from the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology and Engineering (NIMTE), CAS developed a new bio-based polymeric hollow fiber membrane for the use of hemodialysis, which has been proved with excellent dialysis performances, good bio-compatibility and well controlled degradation capacity. The new hollow fiber membrane is promising to be used in hemodialysis and replace the traditional petroleum based polymer membranes.
Polylactide (PLA) possesses better bio-compatibility, lower producing cost, and more importantly, it comes from renewable resources and is independent on petroleum based materials. Moreover, PLA is a polymer that can be buried and degraded after use, which is helpful to reduce the reverse impact on the environment.
 |
| Fig.2 Cross section of PLA hollow fiber |
Up to now, a related patent has been filed (201210547368.0).
Professor Lixin Xue xuelx@nimte.ac.cn
Research Group Url: http://english.nimte.cas.cn/rh/rd/fpm
All Images by ![]()

