The pollution of heavy cations is severely in the water systems such as rivers, lakes, ponds and seas, even if the foods and products. The necessity of a rapid detection method for different types of heavy metal ions is urgent, although there are many ways to detect out the heavy metal cations. Among the existed detection ways for heavy metal cations, they are with some defects: 1) The need of expensive instruments; 2) Tedious pre-treatment procedures for the real samples; 3) Poor selectivity; 4) Low detection sensitivity;5) Long time to obtain the assay results.
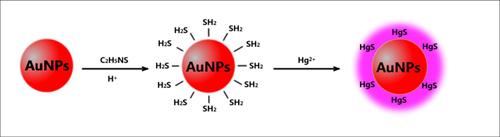
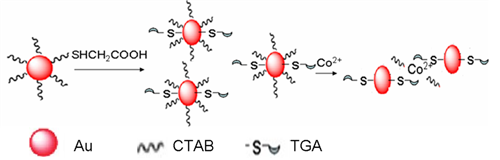
In order to improve the selectivity of the reaction, increase the sensitivity of the reaction and greatly shorten the reaction time, Professor Aiguo Wu’s group from NIMTE CAS used gold nanoparticles as a reaction amplifier to test traditional chemical analysis reactions. This group has been able to rapidly and sensitively detect out many kinds of heavy metal ions through the naked eyes or some simple instruments for example UV-vis spectra. Some related methods have been applied several Chinese patents (Chinese Patent Application Nos.: 200910152440.8; 201010194041.0 and 201010251278.8). Utilizing these methods, this group has obtained the detection limit up to 5 μM observed by the naked eye and 0.486 nM as measured by UV-vis spectra in the test of mercury ions (The upper limit values of mercury in drinking water prescribed by the World Health Organization is: 5 nM). The preliminary results of the related studies have already been published as a full article in Analyst of Royal Society of Chemistry. DOI: 10.1039/clan15113d (http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2011/AN/c1an15113d ). In addition, according to the similar experimental principles, this group also was able to rapidly detect out cobalt ions, the lowest detected concentration is 4.0µM observed by the naked eye and 0.2µM as measured by UV-vis spectra (Nanoscale, DOI: 10.1039/c1nr10149h (http://pubs.rsc.org/en/Content/ArticleLanding/2011/NR/c1nr10149h ); the upper limit values of cobalt in drinking water prescribed by the World Health Organization is: 3.39 μM). The rapid detection of cobalt ions in solution was able to be realized within one minute by this method.
At present, this group has also extended to other cations and tested some environmental samples to confirm that the developing method is suitable to the real samples at the aid of other institutions. The final aim of this group is to develop a convenient detection method which is similar to a pH test paper.
Group Leader Dr. Aiguo Wu aiguo@nimte.ac.cn
|
Fig. 1 A schematic mechanism of Au NPs rapidly sensing of Hg2+ in aqueous solutions |
| (Image by NIMTE) |
 |
|
Fig. 2 A strategyfor Au NPs rapidly sensing of Co2+ in aqueous solutions (Image by NIMTE) |