Printed electronics is a novel technology which applies inkjet, screen printing etc. to produce electronic components. It has the potential of reducing cost, emission and energy consumption compared to the traditional methods, and has received worldwide attention. The Division of Surface Engineering &. Remanufacturing, the Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology &. Engineering (NIMTE) has recently made a series of progress in the development of printable low-cost copper ink, and has published their work on Green Chemistry (Royal Society of Chemistry, IF 5.836) titled Synthesis of highly stable dispersions of nanosized copper particles using L-ascorbic acid,Green Chem., 2011, DOI: 10.1039/C0GC00772B.
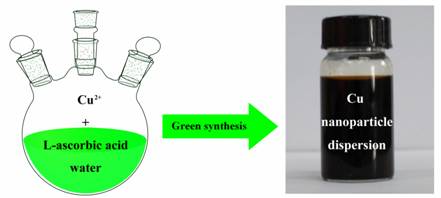 |
| Pic. Green synthesis of copper nanoparticles (Image by NIMTE) |
Printable conductive ink is a key material in printed electronics. Pricy novel metals, such as gold and silver, consist of the majority of conductive inks and often use toxic materials in the production process. Financially supported by the Zhejiang Natural Science Foundation, Xiong Jing, a doctoral candidate and Wang Ye, an engineer OF NIMTE developed an environmental friendly and pollution free synthesis route of highly stable nanosized copper particles. The resulting colloid can be restored in air without oxidization, by using Vitamin C as both the reductant and dressing agent; which paved the way for making copper conductive ink and other applications.
Contacts Wang Ye wangy@nimte.ac.cn

