Thermoelectric (TE) materials can be used to directly convert between heat and electricity through the Seebeck effect and Peltier effect. They usually act as solid state refrigerators and heat pumps without moving parts and environmentally harmful fluids.
Bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) based alloys are one of the most excellent TE materials at room temperature,used commercially for refrigeration and temperature control in fields such as beverage coolers and laser diode coolers. The TE figure of merit (ZT) of commercial Bi2Te3-based alloys is only about 1.0. To increase the efficiency for widely practical applications,materials with higher ZT are desired to be explored.
Recently, the Division of Functional Materials and Nanodevices in Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology &. Engineering (NIMTE) has made a series of progress in nanostructured Bi2Te3-based TE composites.
 |
|
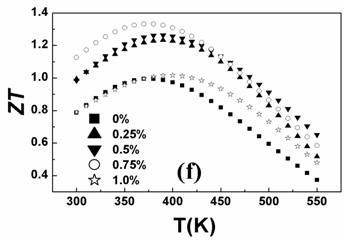
Fig. Temperature dependence of ZT for Bi2Te3-based composites (Image by NIMTE) |
Recently, the Division of Functional Materials and Nanodevices in Ningbo Institute of Materials Technology &. Engineering (NIMTE) has made a series of progress in nanostructured Bi2Te3-based TE composites.
By embedding ZnAlO nanopowder with high electrical conductivity into matrix, p-type Bi2Te3-based TE nanocomposite was prepared using zone melting method. A peak ZT of 1.33 at 370 K was achieved, mainly due to the remarkably increased electrical conductivity and the simultaneously decreased lattice thermal conductivity caused by the introduction of ZnAlO nanopowder. Through the post sintering process, ZT value of this Bi2Te3-based nanocomposite could reach up to 1.4.
The partial work has been published by American Institute of Physics in the journal of Applied Physics Letter (Title: Enhanced thermoelectric performance in p-type BiSbTe bulk alloy with nanoinclusion of ZnAlO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011; 98: 022104.), and the related fabrication techniques have filed a Chinese invention patent (The patent number: 201010291236.7, 201010564073.5). This work was supported by the National Science Foundation of China and the Chinese Academy of Sciences.Contacts
Jun Jiang, Ph.D., Professor jjun@nimte.ac.cn
Ting Zhang, Ph.D. Candidate zhangting@nimte.ac.cn

